Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
i. Define and explain the mole concept, a fundamental unit for measuring matter in chemistry.
ii. Relate gram atomic mass, gram molecular mass, and gram formula mass to mole, understanding their significance in quantifying substances.
iii. Comprehend the connection between Avogadro's number and a mole of any substance.
iv. Distinguish between the terms gram atomic mass, gram molecular mass, and gram formula mass.
v. Convert atomic mass, molecular mass, and formula mass into gram atomic mass, gram molecular mass, and gram formula mass.
Introduction
In the realm of chemistry, measuring matter with precision is crucial for understanding chemical reactions, predicting outcomes, and conducting experiments. The mole concept, a fundamental unit in chemistry, provides a standardized way to quantify matter, enabling scientists to express and manipulate quantities of substances with accuracy and clarity.
i. The Mole Concept: A Counting Unit for Atoms and Molecules
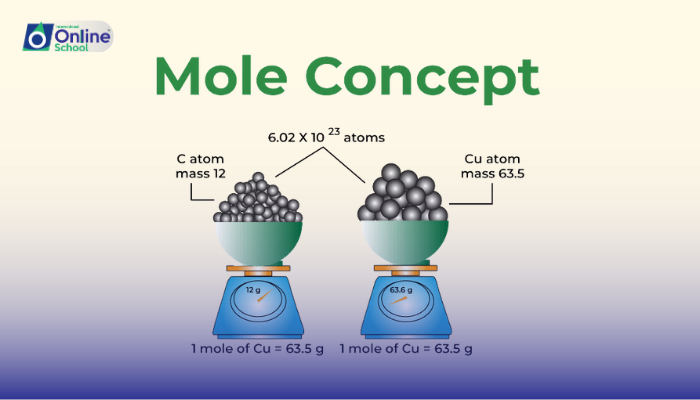
The mole (symbol: mol) is the SI base unit for measuring the amount of a substance. It represents a specific number of particles, known as Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23). Avogadro's number is the same for all substances, regardless of their atomic or molecular mass.
For instance, one mole of water (H2O) contains 6.022 x 10^23 water molecules. This means that a given mass of water can be expressed in moles, providing a more precise and standardized way to quantify the amount of water present.
ii. Gram Atomic Mass, Gram Molecular Mass, and Gram Formula Mass
Gram atomic mass (GAM), gram molecular mass (GMM), and gram formula mass (GFM) are units used to express the mass of one mole of atoms, molecules, and formula units, respectively. These units provide a bridge between the number of particles (moles) and the actual mass of a substance.
Gram atomic mass (GAM): The mass of one mole of atoms of an element. It is equal to the atomic mass of the element expressed in grams. For example, the GAM of carbon (C) is 12 g/mol, which means that one mole of carbon atoms has a mass of 12 grams.
Gram molecular mass (GMM): The mass of one mole of molecules of a compound. It is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule. For instance, the GMM of water (H2O) is 18 g/mol, representing the mass of one mole of water molecules, each composed of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom.
Gram formula mass (GFM): The mass of one mole of formula units of a substance. It is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula unit. While formula units typically represent actual molecules, they may not always do so. For example, the GFM of NaCl (sodium chloride) is 58.44 g/mol, reflecting the mass of one mole of NaCl formula units, each containing one sodium atom and one chlorine atom.
iii. The Connection between Moles and Avogadro's Number
Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23) represents the number of particles (atoms, molecules, or formula units) in one mole of any substance. This fundamental relationship provides a direct link between the mole concept and the actual number of particles present in a given quantity of matter.
In simpler terms, one mole of any substance contains exactly Avogadro's number of particles. This connection is crucial for understanding chemical reactions, where the number of reacting particles determines the extent of the reaction.
iv. Distinguishing Gram Atomic Mass, Gram Molecular Mass, and Gram Formula Mass
The terms gram atomic mass, gram molecular mass, and gram formula mass are often used interchangeably, but there are subtle distinctions between them.
Gram atomic mass: Specific to atoms of an element and is equal to the atomic mass expressed in grams.
Gram molecular mass: Specific to molecules of a compound and is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a molecule.
Gram formula mass: Specific to formula units of a substance, which may not always represent actual molecules, and is equal to the sum of the atomic masses of all atoms in a formula unit.
v. Converting Atomic Mass, Molecular Mass, and Formula Mass to Gram Units
Atomic mass, molecular mass, and formula mass are expressed in atomic mass units (amu), while GAM, GMM, and GFM are expressed in grams. To convert between these units, we multiply the value in amu by the molar.